brinell hardness test indenter material|brinell hardness number chart : mail order According to ISO 6506, the spherical indenter made of hard metal (tungsten carbide) is pressed into a specimen (workpiece) with a defined test load (between 1 kgf and 3000 kgf) to determine the Brinell hardness (HBW). Resultado da 1 de fev. de 2024 · São Jorge Bets Aposta - Slotscalendar. 2024-02-01 2024-02-01 / Cidade. São Jorge Bets Aposta - Slotscalendarjogo robozinho ganhar dinheiropokerstars support emailpixbet 777aviator apostas. Com o avanço da tecnologia, o trabalho online tem se tornado cada vez mais relevante e .
{plog:ftitle_list}
10 de out. de 2023 · Al-Muharaq and El-Zamamra will play their match on 10 Oct 2023 at 01:35. The game will be held on stadium within the North East African League. All interesting information can be found in one place, like Al-Muharaq vs El-Zamamra score, fixtures, statistics, latest score, livescore, and future matches' fixtures.
According to ISO 6506, the spherical indenter made of hard metal (tungsten carbide) is pressed into a specimen (workpiece) with a defined test load (between 1 kgf and 3000 kgf) to determine the Brinell hardness (HBW).
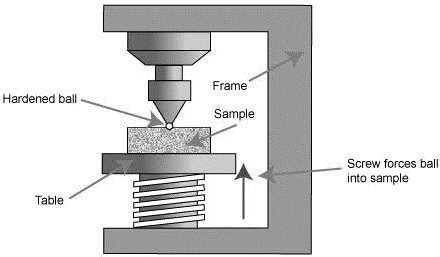
With the Brinell hardness test, a carbide ball is pressed into the material. The indentation surface left behind serves as a measure of the hardness! The factor 0.102 in the equation is due to the unit “kilopond” or .2. Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell test uses a larger spherical indenter, usually made of steel or carbide, and applies a heavy load to the material. The diameter of the indentation is .Indenter sizes: 1, 2.5, 5 and 10 mm. Loads: From 1 kgf to 3000 kgf. Maximum hardness: 650 HBW. A hardness test for larger samples.The Brinell scale / b r ə ˈ n ɛ l / characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science.
Brinell testing often use a very high test load (3000 kgf) and a 10mm diameter indenter so that the resulting indentation averages out most surface and sub-surface inconsistencies. The Brinell method applies a predetermined test load .What is a Brinell Hardness Test? Standards of Brinell Hardness Testing. Brinell Hardness Test Procedure. 1. Preparation of the Specimen. 2. Selection of Load and Indenter. 3. Test Machine Setup. 4. Load Application. 5. Indentation . The Brinell method is a time-honoured approach to assessing the hardness of materials, particularly for larger samples like castings, forgings, and coarse materials. One of .
brinell hardness tester diagram
Indenter shape and material: The indenter is a tungsten carbide metal ball, with a diameter of 1, 2.5, 5 or 10 mm, depending upon the specific Brinell method. Brinell test procedure. In the .Brinell Hardness Test Equations, Calculators and Review . The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science. The typical brinell hardness test uses a 10 millimeters (0.39 in . The Brinell hardness test involves pressing a hard ball indenter, usually made of tungsten carbide, into the material’s surface with a specified force. The diameter of the ball is typically 10 mm, but smaller diameters such .Hardness tests can be defined as forcing an hardness testing indenter of a specified size, shape, and material into the surface of a test piece to obtain a hardness value. Skip to content +1 847-295-6500; . Wilson Brinell .
The Brinell hardness number (BHN or HBW) describes the hardness of a material. The higher the number, the harder the material. The Brinell hardness test involves pressing a small metal ball into the surface of the test material with a known amount of force. The resulting indentation is then measured and converted into a hardness number.
Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell hardness test is named after its inventor, Johan August Brinell. It involves applying a constant load or force to a spherical indenter made of hardened steel or carbide onto the surface of the material being tested. The indentation diameter is then measured optically. EN ISO 6506-1 is a European standard that specifies the requirements for metallic materials' Brinell hardness testing. It outlines the testing method, equipment, calibration, and procedures for determining the Brinell hardness of metallic materials using test forces between 1.96 N and 29420 N. . the testing machines and indenter requirements . Large indenter for average hardness: Not suitable for very hard materials, large indentations: Large parts, castings, forgings: . The Brinell hardness test measures material hardness by determining the diameter of an indentation made by a hardened steel or carbide ball under a specific load. A load, typically ranging from 500 to 3,000 kgf, is .The oldest of the hardness test methods in common use on engineering materials today is the Brinell hardness test. Dr. J. A. Brinell invented this test in Sweden in 1900. . As in the Vickers test, a diamond indenter with a specific geometry is impressed into the specimen surface with a known, calibrated force for a duration of 10–15 sec .
In the standard method of the Brinell Hardness Test, we use 250 to 500 kg of load for soft material and 500 to 3000 kg of load for hard material such as steel and iron. In the standard method of the test, we use a ball indenter of 10mm diameter. Indenter bola baja digunakan untuk material yang memiliki kekerasan Brinell hingga 450 BHN. . Sama halnya dengan hardness test dengan Brinell, karena pengukuran dilakukan secara manual maka terdapat kemungkinan terjadinya kesalahan ukur. Kesalahan itu mungkin terjadi ketika pemfokusan objek pada layar, peletakan alat ukur pada objek dan .Certified Hardness Test Blocks are a requirement as a reference material for any type of hardness testing. Home; Products. . Brinell Hardness Test Blocks — ASTM E-10 and ISO 6506 . It is primarily employed to prevent breaking in brittle materials and to make it easier to measure the hardness of thin layers. The indenter used in the Knoop .
However, it is essential to consider the material's thickness relative to the indenter size. As a general guideline, the material should be at least ten times thicker than the indentation depth to ensure accurate results. If the material is too thin, alternative hardness testing methods, such as Rockwell or Vickers, may be more appropriate .Compared to the other hardness test methods, the indenter used in brinell makes the deepest and widest indentation, so that test averages the hardness over a wider amount of materials which will accounts for multiple grain structures and any irregularities in the uniformity of the material. The Brinell hardness number is defined as the ratio of . ASTM E384: This standard is for hardness testing on a micro-scale, and therefore includes the Vickers and Knoop hardness tests. ISO 6506: This standard mirrors ASTM E10, as it contains the standard method for measuring the Brinell hardness of metals. ISO 6507: This standard contains the details for the Vickers hardness test in metallic materials.
The Brinell hardness test consists of applying a constant load or force, usually between 187.5 and 3000Kgf, for a specified time (from 10 – 30 seconds) typically using a 2.5 or 10mm diameter tungsten carbide ball (see schematic in the .A wide range of materials can be tested using a Brinell test simply by varying the test load and indenter ball size. In the United States, Brinell testing is typically done on iron and steel castings using a 3000 kg test force and a 10 mm diameter ball. . On production welds for P-5 and P-6 group material, a Brinell hardness test should be . Following the oldest method of hardness testing developed by Dr. Johan August Brinell in Sweden in 1900, the Brinell hardness tester presses its indenter into the surface of a material, using a specified load (usually between 500 and 3000 kgf, or kilogram-force) for a period of time known as “dwell time.” Then it measures the diameter of .
The Brinell hardness test uses a ball indenter of diameter, D, which is pressed into the surface of the test piece using a prescribed force, F. The time for the initial application of the force is 2 s to 8 s, and the test force is maintained for 10 s to 15 s. . Metallic materials. Brinell hardness test. Test method: ASTM E10-18: Standard Test .Hardness testing within the realm of materials testing. Today, hardness testing is one of the most widely used methods in mechanical materials testing, especially for metals. On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, density) or to the material behavior under certain stresses (e.g., abrasion . Metode Hardness Test Brinell menggunakan indenter berupa bola yang terbuat dari bahan keras, seperti tungsten karbida. . Dalam analisis kegagalan material, hardness test memiliki peran penting dalam mengidentifikasi penyebab kegagalan dan memahami karakteristik deformasi atau retak yang terjadi pada material. Beberapa dampak pentingnya antara .
The test provides numerical results to quantify the hardness of a material, which is expressed by the Brinell hardness number – HB. The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten .
The diameter of the indentation made on the material’s surface by a spherical indenter—typically a hardened steel ball—is used to calculate the Brinell hardness number (HB). Calculation of Brinell Hardness testing. Brinell hardness testing is used to measure the hardness of materials, particularly metals and alloys.It is an optical method. This means that the size of indentation left by the indenter is measured to determine the hardness value of a test specimen. Indenter shape and material: The indenter is a tungsten carbide metal ball, with a diameter of 1, 2.5, 5 or 10 mm, depending upon the specific Brinell method.The Brinell hardness test of metals and alloys. Engineering ToolBox - Resources, . Brinell Hardness Number vs. Material; Material Brinell Hardness Number; Soft brass: 60: Mild steel: 130: Annealed chissel steel: 235: White cast iron: 415: Nitrided surface: 750: Steel Hardness versus Strength. In the original test proposed by Brinell, the load L is expressed in kilogram force. If L is measured in N (SI system), Eq. 1 should be divided by 9.8065. The full test load is applied for a period of 10–15 s. Two diameters of impression at right angles are measured (usually in the range 2–6 mm), and the mean diameter value is used for calculating the Brinell hardness .
The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from Brinell, and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide).Hardness testing standards have been set by various organisations such as The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and The International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO), prescribing specific varieties of a hardness test determined by factors such as the type of indenter, applied force, and procedure of force application.
brinell hardness test theory
brinell hardness test pdf
Intelligent Tensile Tester wholesalers
Assista ao vídeo. Rio Grande do Sul. Transmissão ao vivo. Últimas Notícias. Globo Notícias . RBS Notícias; Campo e Lavoura; Esporte; Santa Catarina. sul Santa Catarina;
brinell hardness test indenter material|brinell hardness number chart